Microfluidic wound scratching platform based on an untethered microrobot with magnetic actuation
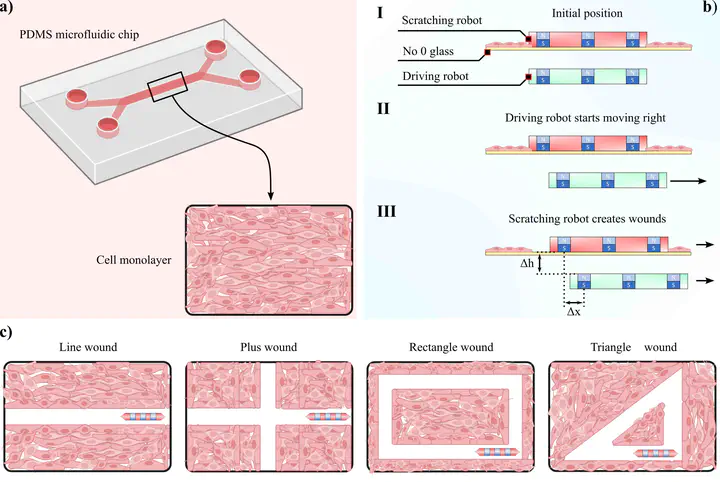 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
Microfluidic chips and a microrobot using SU-8 and NdFeB magnets were fabricated. A faster healing time can be achieved using our method than conventional scratching. Wound’s geometry and shape can influence healing speed and rate. Permanent magnets were successfully coated by PDA, and characterized by SEM and FT-IR. The cell viability is not adversely affected after microrobotic scratching.
Type
Publication
In Sensors and Actuators B Chemical